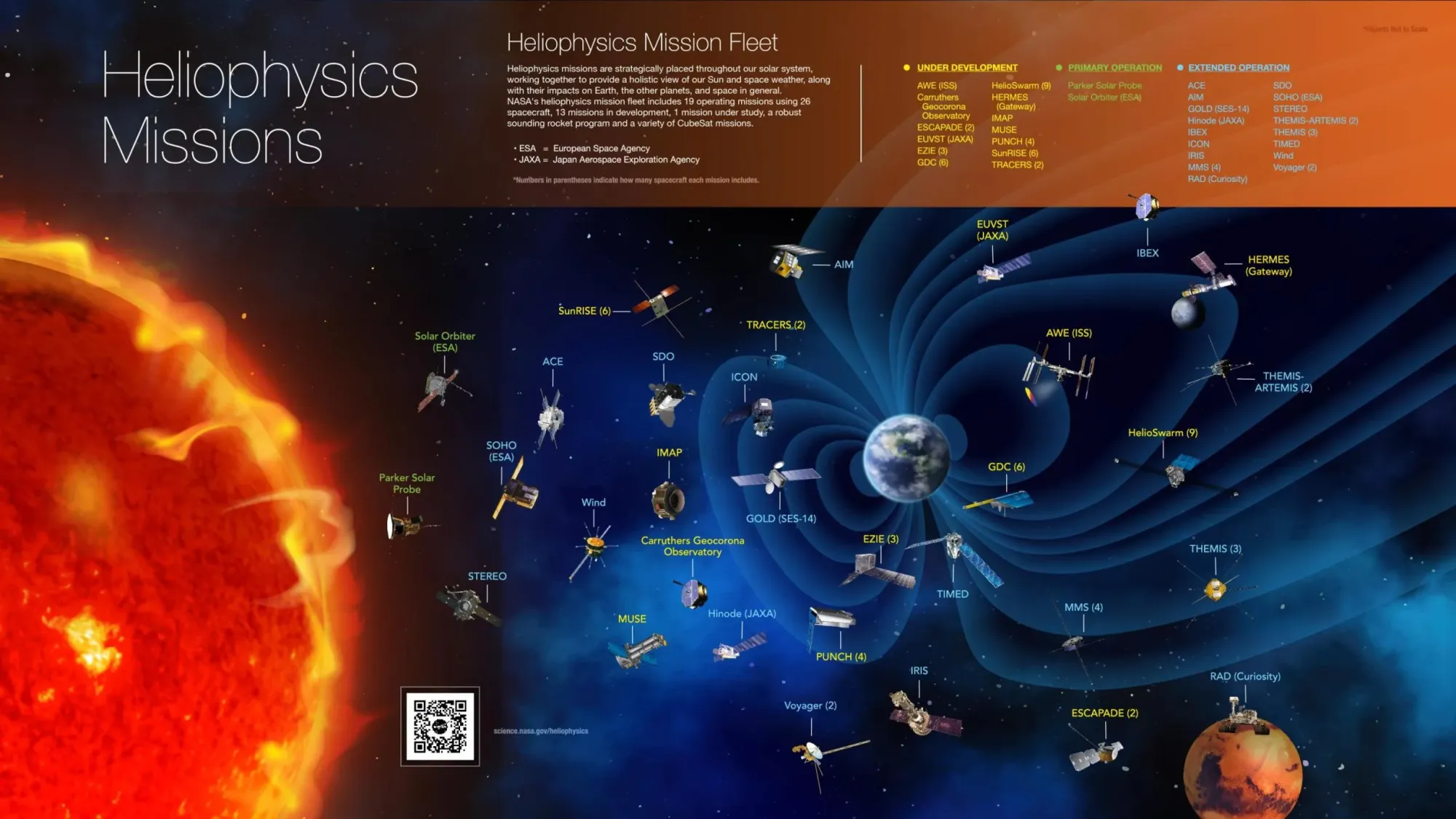
Overview
The Science Mission Directorate Heliophysics Division studies the nature of the Sun, and how it influences the very nature of space — and, in turn, the atmospheres of planets and the technology that exists there. Space is not, as is often believed, completely empty; instead, we live in the extended atmosphere of an active star. Our Sun sends out a steady outpouring of particles and energy -- the solar wind – as well as a constantly writhing magnetic system. This extensive, dynamic solar atmosphere surrounds the Sun, Earth, the planets, and extends far out into the solar system.
Studying this system not only helps us understand fundamental information about how the universe works, but also helps protect our technology and astronauts in space. NASA seeks knowledge of near-Earth space, because -- when extreme -- space weather can interfere with our communications, satellites and power grids. The study of the Sun and space can also teach us more about how stars contribute to the habitability of planets throughout the universe.
Mapping out this interconnected system requires a holistic study of the Sun’s influence on space, Earth and other planets. NASA has a fleet of spacecraft strategically placed throughout our heliosphere -- from Parker Solar Probe at the Sun observing the very start of the solar wind, to satellites around Earth, to the farthest human-made object, Voyager, which is sending back observations on interstellar space. Each mission is positioned at a critical, well-thought out vantage point to observe and understand the flow of energy and particles throughout the solar system -- all helping us untangle the effects of the star we live with.
Heliophysics, also known as heliophysics, is the branch of astrophysics that focuses on the study of the Sun and its interactions with the solar system and beyond. It encompasses the study of various phenomena related to the Sun, solar wind, and their impact on the Earth and other celestial bodies. Here are some key details about heliophysics:
1. Sun as the Central Focus: The Sun is the primary object of study in heliophysics. Scientists in this field seek to understand the Sun's structure, dynamics, and behavior, as well as the various processes that occur within and around it.
2. Solar Wind: One of the central concepts in heliophysics is the solar wind, which is a continuous stream of charged particles (mostly electrons and protons) that are ejected from the Sun's outer layers into space. Understanding the solar wind and its variations is crucial for predicting space weather and its effects on Earth and other planets.
3. Space Weather: Heliophysicists study space weather, which refers to the conditions in space influenced by the Sun. Space weather can have significant impacts on satellite communications, navigation systems, power grids, and even human health during space missions. Researchers aim to predict and mitigate the effects of space weather events like solar flares and geomagnetic storms.
4. Magnetospheres and Ionospheres: Heliophysicists also investigate the magnetospheres and ionospheres of planets, including Earth. These regions of a planet's atmosphere are influenced by the interaction between the planet's magnetic field and the solar wind. Understanding these interactions is vital for planetary science and space exploration.
5. Solar Observations: Scientists use various instruments and spacecraft to observe the Sun, including solar telescopes and solar observatories. These observations provide valuable data on solar activity, such as sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
6. Space Missions: Space agencies like NASA and ESA (European Space Agency) have launched numerous spacecraft to study the Sun and heliophysics phenomena. Examples include the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO), the Parker Solar Probe, and the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO).
7. Interdisciplinary Field: Heliophysics is highly interdisciplinary, involving elements of astrophysics, plasma physics, magnetospheric physics, and planetary science. Researchers in this field collaborate across disciplines to gain a comprehensive understanding of the Sun's impact on the solar system.
8. Ongoing Research: Heliophysics is an active and evolving field of research. Scientists continue to develop new models, theories, and observational techniques to better understand the Sun and its interactions with the solar system. This knowledge is essential for space exploration, satellite operations, and space science in general.
In summary, heliophysics is the scientific discipline that explores the Sun's behavior, solar wind, space weather, and their effects on the solar system. It plays a critical role in our understanding of space environments and their impacts on technology and human activities in space.